ULTRASOUND CONTRAST AGENT MICROBUBBLES
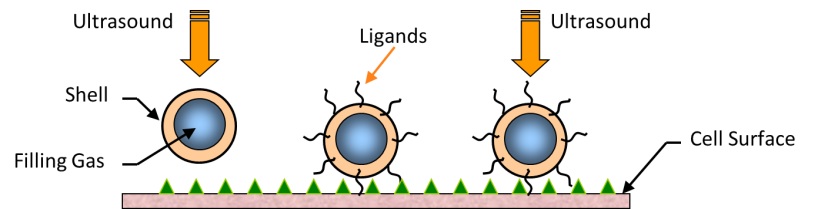
Schematic diagram depicting the interaction of contrast agent microbubbles with ultrasound near a cell surface. Ultrasound helps drive the contrast agent - comprised of a gas bubble stabilized with an outer shell - to the cell surface. In some cases, ligands can be attached to the outer surface of the contrast agent to help them adhere to the cell membrane and target specific tissues.
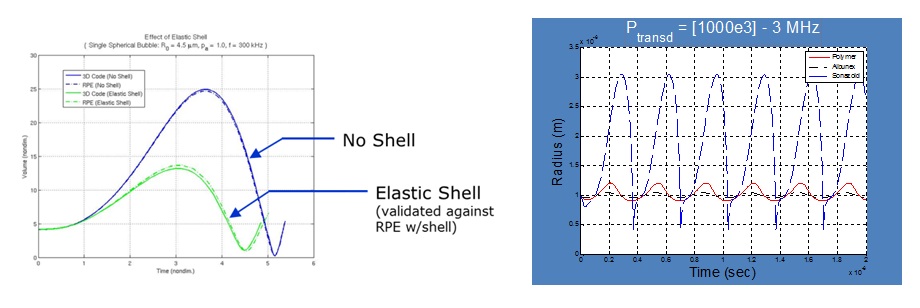
The figure on the left depicts the influence of a shell on the volumetric expansion of a microbubble. The shell stiffens the bubble and reduces the maximum volume. The figure on the right shows computational simulations of the dynamic response of various commercially-available contrast agents. The different shell properties account for the variation in radial response.
Copyright 2012, Ross Elder